Resist Process Information
PMMA Process Information
NOTE! We stock two different Molecular Weights of PMMA, 495K and 950K -- they are NOT interchangeable. 495K generally has lower dose. The two can be used together in a bi-layer process to provide a good undercut profile for liftoff.
All of our PMMA is in Anisole solvent. We do not have any PMMA dissolved in chlorobenzene.
The viscosity of the resist dilution, along with the spin speed, determine the thickness of the resist film. To obtain a wide range of thicknesses, we stock many different viscosities of PMMA. For PMMA, the dilution is expressed in percent solids dissolved in anisole; thus "A5" is a 5% dilution of PMMA in Anisole.
Dilutions
Here are the PMMA dilutions at the WNF:| 495K | 950K |
|---|---|
| 1.5 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 2 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 6 | 5 |
| 8 | 6 |
| 9 | |
| 11 |
Spin-Speed Thickness Data
For the spin-speed data on this page, the black-and-white graphs from the Microchem documentation; the color graphs are my own measured data.495K PMMA
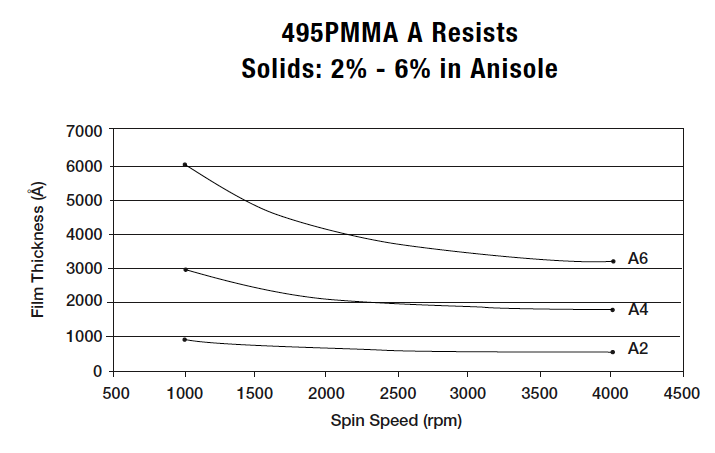
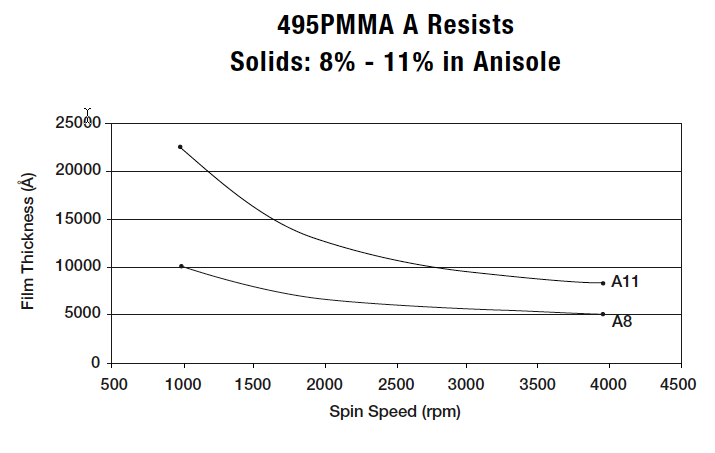
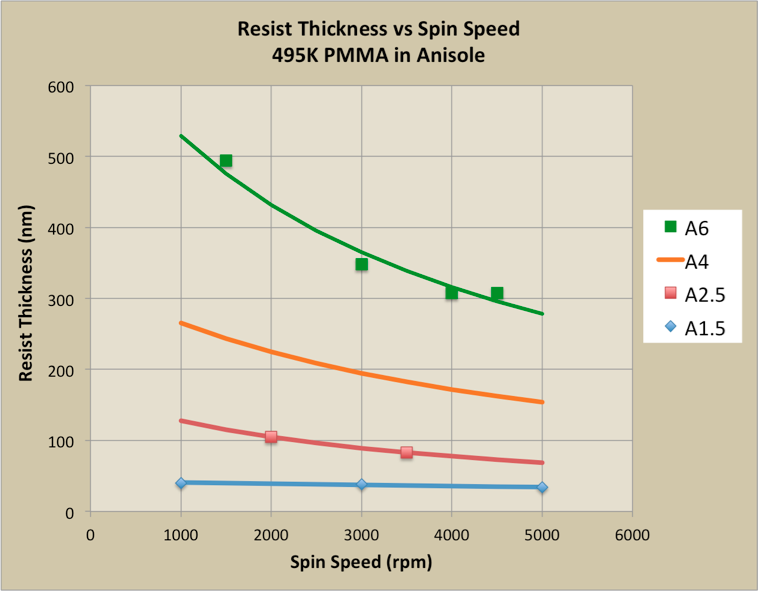
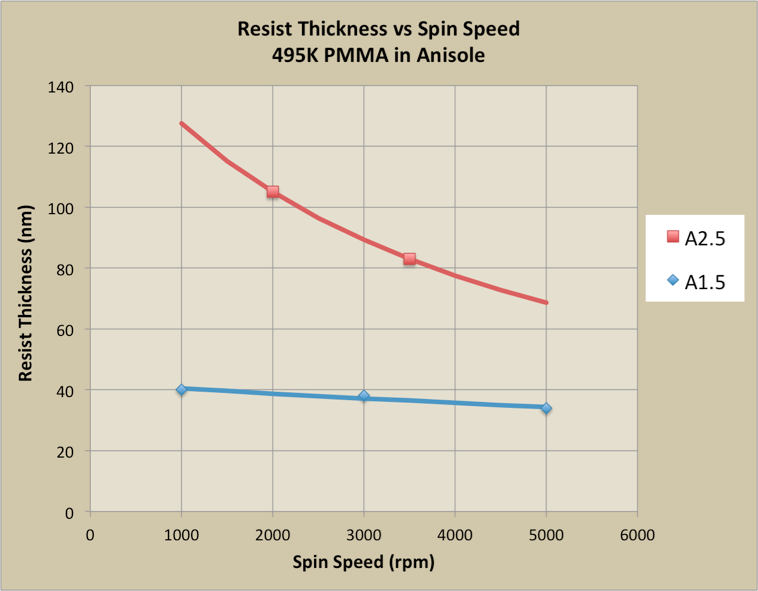
PMMA 950K


Typical Process Parameters
1. Dispense resist, covering about 1/3 to 1/2 of sample diameter2. Spin resist, 60 seconds (longer, 90 or 120 seconds for very thick coatings)
3. Bake resist, hotplate, 180 C, 60-180 seconds.
4. Expose. Dosing ranges from 250-750 µC/cm^2, depending on substrate, feature size and density.
5. Develop. 30-90 seconds, MIBK:IPA, 1:1 or 1:3 (1:1 = lower dose, lower contrast, 1:3 = higher dose, higher contrast)
6. Rinse, IPA, 15 seconds. N2 dry.
Process Notes
- In general, PMMA has excellent adhesion to most materials.
- HMDS does not generally help adhesion. Cleaning the substrate with piranha or an O2 plasma (ie, barrel ash) will help adhesion.
- PMMA has generally poor etch resistance
- PMMA can be stripped in NMP (best), Acetone (ok), or an O2 plasma
- When stripping or during liftoff, be sure to keep the substrate completely wet at all times, until after final rinsing in IPA is completed, or you will have a hard-to-remove residue.
Vendor Information
See also, the Microchem PMMA application guide
